
On November 15 2017, Airbus signed a deal with Indigo Partners in Phoenix, Arizona to sell 430 A320neo family aircraft. On October 15 2014, IndiGo acquired 250 A320neo family aircraft. On March 15, Turkish Airline ordered 4 A320neo. EasyJet, a British low-cost airline planned to purchase 100 A320neo to be delivered from 2017 to 2022. On March 14 2013, Lufthansa ordered 70 A320neos. In December, Pegasus Airlines had a firm order for 57 units of A320neo. postponed the delivery of the aircraft until 2020. In November of the same year, Virgin America Inc. On January 25 2012, Norwegian, the third largest low-cost carrier in Europe committed to order 100 A320neo. On July 27, Lufthansa placed an order for 25 A320neo. On July 20 2011, American Airlines ordered 130 aircraft. On January 17, Virgin America Inc., an American airline from 2007 to 2018 ordered 30 aircraft.

In January 2011, IndiGo, a low-cost carrier in India signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for 150 orders of A320neo. The aircraft was designed with a special logo, “First to fly A320neo”. It took off from the Airbus facility in Hamburg, Germany with flight number LH9917. On January 25 2016, the A320neo entered into service and was introduced by Lufthansa, the launch operator of the aircraft. Trevor Woods, the EASA’s Certification Director, while the FAA certificate by the FAA Manager of Transport Airplane Directorate- Aircraft Certification Service, Mr. On November 24 2015, the A320neo received its joint certification from the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). On September 25 2014, the aircraft took its maiden flight from Toulouse. On July 1 2014, the company has rolled out its first A320neo equipped with Pratt and Whitney PW1100G engines in Toulouse, France. Unlike NEO which is indivisible (meaning the smallest unit of NEO will always be 1) GAS tokens are divisible and generated by a decay algorithm.The A320neo was launched by Airbus on December 1 2010.

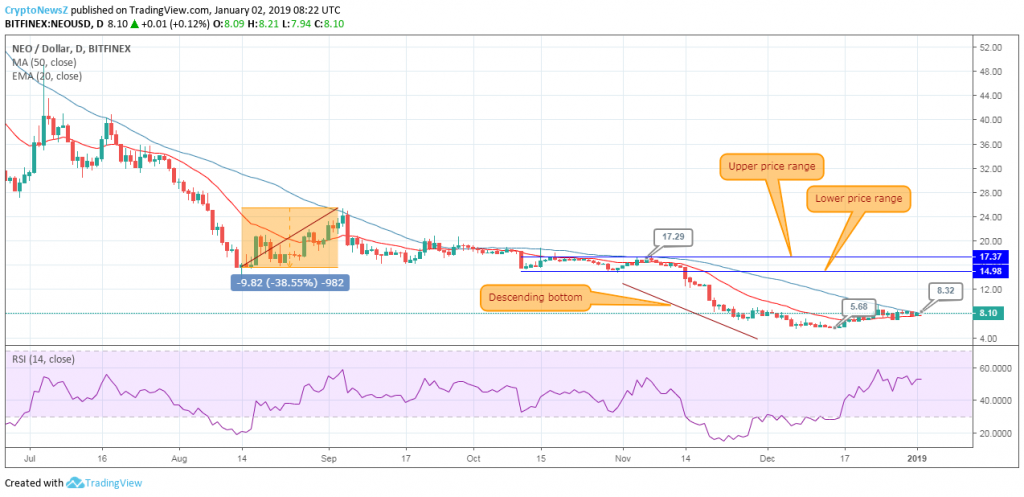
The supply of NEO is thus limited to 100 million units. Since Neo uses a Proof of Stake system to validate transactions, it is only possible for users to earn NEO by staking their tokens to help validate transactions rather than the mining that takes place in Proof of Work systems.

Staking NEO grants users a portion of the block rewards, paid in the platform’s second token, GAS.GAS tokens are used to pay for transactions on the network as well as for running Dapps. Those who stake NEO also then have the right to vote on upgrades to the network’s parameters. NEO is the platform’s primary token which powers the Neo blockchain and can be used for holding, sending, spending, and staking. NEO in practice The Neo network has two native tokens: NEO and GAS. The use of digital identities helps to protect Neo’s users from scams and will make it easier for Neo to comply with international law. This compliance applies even to the various nodes on the network which need to have identification before they can contribute to the transaction verification and other activities like accounting and bookkeeping. Users have the option to transact among themselves only if the other party has the required identity, which makes the Neo network regulatory-compliant. Neo distinguishes itself from other blockchain platforms by increasing focus on regulatory compliance, it emphasizes this compliance through the creation of a key feature called “digital identity.” Every individual, business, or other entity operating on the Noe platform is required to have a unique digital identity that can be verified. Neo’s goal is to automate the management of digital assets through the use of smart contracts, with the eventual aim of building a distributed network-based smart economy system. A brief history Neo, formerly known as Antshares (ANS) was founded by Da Hongfei and Erik Zhan in China in 2014 and rebranded as Neo in June 2017.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
